◄ Carnets Geol. 13 (A07) ►
[1) Introduction]
[2) Material and method]
[3) "Acroporella occidentalis"]
[4) Cymopolia mayaense & , 1965]
[5) Cylindroporella elassonos & , 1965]
[6) Conclusions]
[Bibliographic references] and ... [Plates]
Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, The
University of Kansas, 1200 Sunnyside Avenue, Lawrence, Kansas 66045 (USA)
Kralja Petra I, 38, 11000, Beograd (Serbia)
Ivan Rakovec Paleontological Institute, ZRC SAZU, Novi trg 2, 1000 Ljubljana (Slovenia)
Manuscript online since November 11, 2013
[Scientific editor:
Michel ; technical editor: Bruno ;
language editor: Stephen ]
This first report is a revision of fossil calcareous green algae (Dasycladales) described from the Upper Cretaceous and Paleocene series of Guatemala. Among other things in their 1965 paper J.H. and H.V. introduced three new species originally referred to the genera Acroporella, Cylindroporella, and Cymopolia. One species, which has previously been referred to the genus Cylindroporella, is a foraminifer.
Paleocene; Upper Cretaceous; Guatemala; Dasycladales.
B., R. & K. (2013).- Revision of the Jesse Harlan Collection. Part 1. Some fossil Dasycladales from Guatemala.- Carnets de Géologie [Notebooks on Geology], Brest, Article 2013/07 (CG2013_A07), p. 281-301.
Révision de la Collection Jesse Harlan . Première partie. Quelques Dasycladales fossiles du Guatémala.- Ce premier rapporte traite de la révision de quelques algues calcaires vertes fossiles (Dasycladales), ou supposées telles (dans les faits un de ces taxons attribué au genre Cylindroporella est un foraminifère), décrites de terrains crétacés et paléocènes du Guatémala. Dans leur papier de 1965 J.H. and H.V. avaient entre autres choses introduit trois nouvelles espèces attribuée à l'origine aux genres Acroporella, Cylindroporella et Cymopolia.
Paléocène ; Crétacé supérieur ; Guatémala ; Dasycladales.
Jesse Harlan (1892-1974) was a prolific American paleophycologist (, 1977, 1985; anonymous, last consulted 2013-09-24) who described a number of fossil algal taxa, both red and green "calcareous algae", including mostly new species, but less commonly new genera. Several years after his death part of his collection, which was then located at the Colorado School of Mines in Golden, was transferred to the University of Kansas at Lawrence. Another significant part of his collection, i.e., the specimens bearing U.S. National Museum labels in his publications, is stored at the Smithsonian Institution in Washington D.C.. One cannot exclude the possibility that further specimens might be in some geological survey, but the core of the collection (the potential "types") was sent to the Smithsonian awaiting paleophycologists to check this reference material. During the course of a short-term visit the first author (B.G.) was given the opportunity to access this collection and to study part of this material. The following report is the first of a forthcoming series dedicated to Jesse Harlan 's fossil calcareous algae. It deals with three "species" described in and (1965): "Acroporella occidentalis", a nomen nudum (see discussion in & , 1992, and herein), Cymopolia mayaense & , 1965, and Cylindroporella elassonos & , 1965.
With respect to these taxa, and (1965) list four thin sections with an USNM registration number (No. 42499, 42500, 42504, and 42524, ink writing, which correspond respectively to locality numbers 4819, 4819(2), 7747, and 10029, glass engraving). However the thin section 42500 is probably lost as there is no record for it in the Smithsonian Institution's inventory. The quality of the remaining thin sections varies significantly: the color of the Canada balsam has locally turned from light yellow to dark brown; the rock slices themselves have different thicknesses; the sections of the fossil specimens are random; etc.
The microfacies of slide 42499 is bioturbated bioclastic wackestone with benthic foraminifers and calcareous green algae. Slide 42524 is also a bioturbated foraminiferal wackestone, but it has suffered some diagenetic alteration. The last slide, i.e., No. 42504, consists of a chloralgal grainstone with the typical circumgranular fibrous cementation that characterizes submarine hardground formation (the remaining intergranular pore space is occluded by a late phreatic drusy cement).
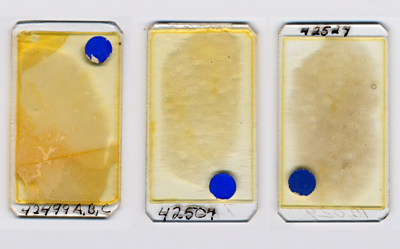
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
Figure 1: The three (remaining) thin sections studied.
According to &
(1992), this taxon is a nomen nudum because its type was not properly identified. Actually, &
(1965, p. 78) clearly state that the type slide is "4819 = U.S.N.M. No. 42499" and illustrate two sections of the algal thallus ("Plate 7, figures 1, 2"; herein Fig.
2 ![]() ).
In the figure caption of their Plate 7, none of the sections is explicitly defined as the type-specimen (holotype or type) or even referred to the type slice.
).
In the figure caption of their Plate 7, none of the sections is explicitly defined as the type-specimen (holotype or type) or even referred to the type slice.
We found that none of these figured algal sections occurs in the type slice. Accordingly, none can be considered as a potential candidate to be selected as the lectotype. None of them are visible on the second thin section, even though & (1965, p. 78) state that slide "7747 = U.S.N.M. No. 42504" was also figured. In conclusion, both illustrated sections probably come from a third slide, labelled "4819(2) = U.S.N.M. No. 42500". Because this last slice is lost, this material (corresponding to the printed photomicrographs), which otherwise could have been considered as syntypes, cannot be used to define a lectotype. At this stage there are two options remaining:
1) we select a neotype from the type slice and therefore we keep the original specific epiteth, i.e., "occidentalis";
2) alternatively we could select an holotype (and paratypes) and give a brand new name to these specimens. In the same paper, & (1965) have already introduced three new species all bearing "occidentalis" as a specific epithet (one Jania, one Larvaria and the "Acroporella").
We retained the first option in order to avoid further confusion. This option implies that both the date of valid publication (2013 in lieu of 1965) and the authorship of the species change. Following (1990) we shall not refer the species to the Triploporellacean genus Acroporella , 1964, but to the Polyphysacean genus Clypeina (, 1845), that already includes more than 40 species (see & , 1992; & , 1993, 1994; and , 2013, for a recent addition to the list).
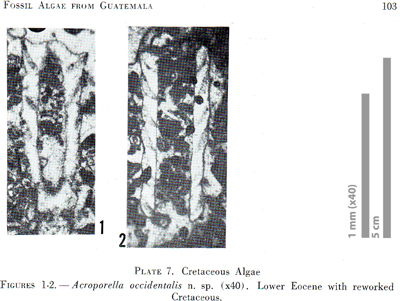
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
Figure 2: Duplicate of "Plate 7, figures 1, 2" in & (1965) with "Acroporella occidentalis". Some rights reserved.
Phylum Chlorophyta
Class Dasycladophyceae et al., 1995
Order Dasycladales , 1931
Family Polyphysaceae (, 1841)
Tribe Clypeineae (, 1968)
Genus Clypeina (, 1845)
Clypeina occidentalis & in et al., 2013
[= Clypeina occidentalis & ex & in et al., 2013, non 1965]
(Fig. 2 ![]() ;
Pl. 1
;
Pl. 1 ![]() , figs. a-f;
Pl. 2
, figs. a-f;
Pl. 2 ![]() , figs. a-l;
Pl. 3
, figs. a-l;
Pl. 3 ![]() , figs. a-j;
Pl. 4
, figs. a-j;
Pl. 4 ![]() ,
figs. a-c; Pl. 8
,
figs. a-c; Pl. 8 ![]() ,
fig. d)
,
fig. d)
Neotype (selected herein): Pl. 2 ![]() , fig. b. This specimen is an oblique section with three successive verticils. Thin section USNM 42499 (=4819, see
Fig. 1
, fig. b. This specimen is an oblique section with three successive verticils. Thin section USNM 42499 (=4819, see
Fig. 1 ![]() ).
).
Paratypes: all the accompanying sections from the same material (Pl. 1 ![]() , figs. a-f;
Pl. 2
, figs. a-f;
Pl. 2 ![]() , figs. a-l;
Pl. 3
, figs. a-l;
Pl. 3 ![]() , fig. a)
, fig. a)
Measurements: The new measurements for the external diameter of the calcareous coating (D), the internal diameter (d) and their relative ratio (d/D) are displayed in the table below. Blue (cyan) cells for data measured on slide 42499, green (lime) cells for slide 42504, yellow cells for the combination of both slides.
| Clypeina occidentalis | D µm | d µm | d/D % |
| 42499 (=4819) | 438 | 171 | 39% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 400 | 210 | 52% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 476 | 210 | 44% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 571 | 286 | 50% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 495 | 200 | 40% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 571 | 190 | 33% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 476 | 171 | 36% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 429 | 190 | 44% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 524 | 162 | 31% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 381 | 190 | 50% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 571 | 324 | 57% |
| average ALL (11 measur.) | 485 | 210 | 43% |
| standard deviation (σ) | 66 | 50 | 8% |
| average 42499 (9 measur.) | 487 | 199 | 41% |
| standard deviation (σ) | 66 | 50 | 7% |
In the type slide, D = ca. 490 +/- ca. 65µm and d = ca. 200 +/- ca. 50µm for a ratio d/D = 41 +/- 7%. The
maximum length is 2.0mm
(Pl. 1 ![]() , fig. a) and the spacing of the whorls (including the height of a whorl) is quite variable, ranging from 190 to 380µm. The "pores" (laterals) gradually
increase in diameter from 50µm in the proximal part to 80µm in the distal part. There are usually 12 laterals per verticil (but this number may vary from ten to
twenty). These laterals arise at steep angle (ca. 30°) along the main axis. Because they are commonly abraded distally, they are in average 170µm in length but, in better preserved specimens
(Pl. 1
, fig. a) and the spacing of the whorls (including the height of a whorl) is quite variable, ranging from 190 to 380µm. The "pores" (laterals) gradually
increase in diameter from 50µm in the proximal part to 80µm in the distal part. There are usually 12 laterals per verticil (but this number may vary from ten to
twenty). These laterals arise at steep angle (ca. 30°) along the main axis. Because they are commonly abraded distally, they are in average 170µm in length but, in better preserved specimens
(Pl. 1 ![]() , fig. f;
Pl. 2
, fig. f;
Pl. 2 ![]() , fig. b), they may reach 350µm.
, fig. b), they may reach 350µm.
Discussion: The general morphological features, the measurements, and last, but not least, both their stratigraphic ranges
[1] and their geographic locations [2] point to synonymize this species (now validly published) with Clypeina elliotti J.-P. & R. ,
1966 (op. cit., Pl. 11, figs. 155-159). When writing their manuscript the latter authors were
unaware of the existence of a "competitor". Later, in a postscript note ( J.-P. & R.,
1966, p. 41), they acknowledge the contribution newly published by & (September
1965). We understand that, on the basis of the poor illustration of "Acroporella occidentalis" ( & ,
1965, Pl. 7, figs.
1-2; herein Fig.
2 ![]() ), they could not
considered a possible synonymy with their new species.
), they could not
considered a possible synonymy with their new species.
[1] "Lower Eocene" for Clypeina occidentalis versus "Paleocene (or lower Eocene ? )" for Clypeina elliotti.
[2] Guatemala for Clypeina occidentalis versus Cuba for Clypeina elliotti.
According to &
(1965, p. 85), the type slide is "4819 = U.S.N.M. No. 42499" but none of their illustrated specimens (op. cit., Pl. 18, figs.
1-4; herein Fig. 3.1-4 ![]() ) occurs precisely in this thin section. They say they "also figured slide" (..) "4819(2) = U.S.N.M. No. 42500" but one should not forget that this last slice is lost. Fortunately, we identified one photomicrograph ( & ,
1965, Pl. 18, fig. 3) as originating from a capture of slide "7747 = U.S.N.M. No. 42504". It includes several sections, which can be treated as syntypes, and one of them will be selected as the lectotype.
) occurs precisely in this thin section. They say they "also figured slide" (..) "4819(2) = U.S.N.M. No. 42500" but one should not forget that this last slice is lost. Fortunately, we identified one photomicrograph ( & ,
1965, Pl. 18, fig. 3) as originating from a capture of slide "7747 = U.S.N.M. No. 42504". It includes several sections, which can be treated as syntypes, and one of them will be selected as the lectotype.
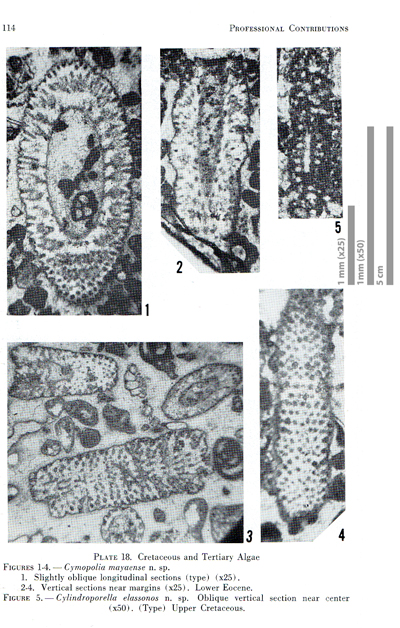
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
Figure 3: Duplicate of "Plate 18" in & (1965) with Cymopolia mayaense and "Cylindroporella elassonos". Some rights reserved.
Phylum Chlorophyta
Class Dasycladophyceae et al., 1995
Order Dasycladales , 1931
Family Dasycladaceae , 1843
Tribe Dasycladeae , 1920
Sub-Tribe Cymopoliinae (, 1931)
Genus Cymopolia J.V. , 1816
Cymopolia mayaense & , 1965
(Fig. 3.1-4 ![]() ;
Pl. 4
;
Pl. 4 ![]() , figs. d-f;
Pl. 5
, figs. d-f;
Pl. 5 ![]() , figs. a-i;
Pl. 6
, figs. a-i;
Pl. 6 ![]() , figs. a-c;
Pl. 7
, figs. a-c;
Pl. 7 ![]() , figs. a-f;
Pl. 8
, figs. a-f;
Pl. 8 ![]() , fig. e)
, fig. e)
Synonymy list:
1965 Cymopolia mayaense n.sp.- & , p. 83-85, Pl. 18, figs. 1-4
("type": Pl. 18, fig. 1; herein Fig. 3.1);
1966 Cymopolia cf. kurdistanensis .- J.-P. & R. , p. 38, Pl. 11, figs. 165-167;
non 1968 Cymopolia mayaense.- , p. 385, Pl. (3) [Pl. h.-t. XVIII], fig. 5;
non 1978 Cymopolia mayaense.- & , p. 71-72, Pl. 7, figs. 3-4;
1982 Cymopolia mayaense.- & , p. 68-69, Pl. 5, fig. 3 (= Pl. 18, fig. 1 in & , 1965);
1992 Cymopolia mayaense.- & , p. 344 (not illustrated);
1998 Cymopolia mayaense.- , p. 76-77, Pl. 11, figs. 1-6; Pl. 12, figs. 1-2; Pl. 13, fig. 1
Lectotype (selected herein): Pl. 6 ![]() , fig.
b pars. This is the tangential section at the bottom of the figure, which shows (?) 12 successive verticils, already illustrated by &
(1965, Pl. 18, fig. 3 pars; herein
Fig. 3.3
, fig.
b pars. This is the tangential section at the bottom of the figure, which shows (?) 12 successive verticils, already illustrated by &
(1965, Pl. 18, fig. 3 pars; herein
Fig. 3.3 ![]() pars). Thin section USNM 42504 (=7747, see Fig. 1
pars). Thin section USNM 42504 (=7747, see Fig. 1 ![]() ).
).
Paratypes: Pl. 6 ![]() , fig.
b pars, the accompanying random sections from the same photomicrograph, already illustrated by &
(1965, Pl. 18, fig. 3 pars; herein Fig.
3.3
, fig.
b pars, the accompanying random sections from the same photomicrograph, already illustrated by &
(1965, Pl. 18, fig. 3 pars; herein Fig.
3.3 ![]() pars). Thin section USNM 42504 (=7747).
pars). Thin section USNM 42504 (=7747).
Measurements: The new measurements for D, d and d/D are given in the table below. Blue (cyan) cells for data measured on slide 42499, green (lime) cells for slide 42504, yellow cells for the combination of both slides.
| Cymopolia mayaense | D µm | d µm | d/D (%) |
| 42499 (=4819) | 381 | 171 | 45% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 876 | 371 | 42% |
| 42499 (=4819) | 676 | 305 | 45% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 705 | 295 | 42% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 381 | 124 | 33% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 714 | 248 | 35% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 724 | 248 | 34% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 619 | 286 | 46% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 762 | 381 | 50% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 905 | 381 | 42% |
| 42504 (=7747) | 457 | 171 | 38% |
| average ALL (11 measur.) | 655 | 271 | 41% |
| standard deviation (σ) | 180 | 89 | 6% |
| average 42504 (8 measur.) | 658 | 267 | 40% |
| standard deviation (σ) | 169 | 91 | 6% |
In the slide 42504, D = ca. 660 +/- ca. 170µm and d = ca. 270 +/- ca. 90µm for a ratio d/D = 40 +/- 6%. The
maximum length is 2.4mm
(Pl. 5 ![]() , fig. b) and the interwhorl spacing (including the height of a whorl) ranges from 120 to 170µm. There are some 20 laterals per verticil. The sterile primary or secondary orders of the laterals rarely exceed 40µm in diameter. The subspherical fertile ampulla (they are ovoidal to ellipsoidal in Cymopolia heraki , 1967: see Pl. II, fig. 10 op. cit., for instance) in terminal position on a primary and surrounded by 4 to 6 secondaries reaches 100µm in diameter.
, fig. b) and the interwhorl spacing (including the height of a whorl) ranges from 120 to 170µm. There are some 20 laterals per verticil. The sterile primary or secondary orders of the laterals rarely exceed 40µm in diameter. The subspherical fertile ampulla (they are ovoidal to ellipsoidal in Cymopolia heraki , 1967: see Pl. II, fig. 10 op. cit., for instance) in terminal position on a primary and surrounded by 4 to 6 secondaries reaches 100µm in diameter.
Discussion: With an outer diameter D = ca. 660 +/- ca. 170µm and an inner diameter d = ca. 270 +/- ca. 90µm (in the slide 42504), this species is by far the smallest of all the Cenozoic representatives of the genus Cymopolia. Being the smallest, it also has proportionally a lesser number of laterals per verticil than the larger Cymopolia elongata (, 1825), for instance (see & , 1982). Again, material described from Cuba by J.-P. & R. (1966, Pl. 11, figs. 165-167) as "Cymopolia cf. kurdistanensis " is very similar, if not identical, to the material from Guatemala.
&
(1965) illustrated under their "Plate 18, figure 5"
(Fig. 3.5 ![]() ) the "Type" of their "Cylindroporella elassonos n.sp.". They give a perplexing and puzzling "Description" (op. cit., p. 82) and also refer to a type "Slide 10029 = U.S.N.M. No. 42524"
(Fig. 1
) the "Type" of their "Cylindroporella elassonos n.sp.". They give a perplexing and puzzling "Description" (op. cit., p. 82) and also refer to a type "Slide 10029 = U.S.N.M. No. 42524"
(Fig. 1 ![]() ). There are no bioclasts referable to algae in this slide. We examined it and were able to capture a new image
(Pl. 8
). There are no bioclasts referable to algae in this slide. We examined it and were able to capture a new image
(Pl. 8 ![]() , fig. a). The so-called "Cylindroporella" is a foraminifer, probably a Dicyclina sp. (or a Cuneolina sp.), but not an alga. The thin section includes more specimens
(Pl. 8
, fig. a). The so-called "Cylindroporella" is a foraminifer, probably a Dicyclina sp. (or a Cuneolina sp.), but not an alga. The thin section includes more specimens
(Pl. 8 ![]() , figs. b-c) of these agglutinated foraminifers, which are rather common in Upper Cretaceous shallow-water carbonate facies.
, figs. b-c) of these agglutinated foraminifers, which are rather common in Upper Cretaceous shallow-water carbonate facies.
Among the three taxa introduced by & (1965), 1) only one species, i.e., Cymopolia mayaense, passed the re-evaluation. We selected a lectotype out of the syntypes to replace its original holotype, which is lost. 2) Another species, i.e., "Acroporella occidentalis", was not validly published by lack of a correct definition of its holotype. We selected a neotype for the combination Clypeina occidentalis, but because the year of reference is 2013 (not 1965) it now proves to be a junior synonym of Clypeina elliotti J.-P. & R. , 1966. 3) The last one, i.e., "Cylindroporella elassonos", is actually not an alga but a foraminifer.
The stratigraphic range of the Cenozoic species, i.e., Clypeina occidentalis and Cymopolia mayaense,
is restricted to the Paleocene on the basis of the foraminiferal assemblage that includes:
1) Pseudorhapydionina moulladei ,
1995 (quoted as "Rhapydionina" by & ,
1965), in both thin sections [Pl. 2 ![]() , fig. f;
Pl. 4
, fig. f;
Pl. 4 ![]() , figs. d & f;
Pl. 5
, figs. d & f;
Pl. 5 ![]() , fig. f;
Pl. 8
, fig. f;
Pl. 8 ![]() , figs. g & j];
2) "Quasiborelis" floridanus ()
[Pl. 4
, figs. g & j];
2) "Quasiborelis" floridanus ()
[Pl. 4 ![]() , fig. f] and Kayseriella cf. decastroi
[Pl. 8
, fig. f] and Kayseriella cf. decastroi
[Pl. 8 ![]() , fig. i] in thin section 42504;
3) Idalina cf. sinjarica and Haymanella sp. in thin section 42499.
, fig. i] in thin section 42504;
3) Idalina cf. sinjarica and Haymanella sp. in thin section 42499.
This first contribution to the revision of the Jesse Harlan Collection demonstrates the necessity to maintain palaeophycological reference collections, primarily as reference material, but also because of the increase in our knowledge, to re-examine these algal microfossils.
The first author (BG) benefited from a Smithsonian Fellowship allowing him to investigate the J. Harlan Collection stored in the premises of the Smithsonian Institution. This research was also partly sponsored by the Association "Carnets de Géologie". He would like to thank the staff of the Department of Paleobiology at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History and particularly William A. and Jonathan G. for their hospitality and having facilitated his work there, Una for having provided information on Collection at the Biodiversity Institute of the University of Kansas in Lawrence, as well as Vlasta for early suggestions regarding the associated benthic foraminifers. Finally he also acknowledge the positive comments and suggestions of a friendly group of paleophycologists that includes Filippo , Ioan I. , Marc André and Felix .
anonymous (last consulted 2013-09-24).- J. Harlan Collection, Kansas Collection, RH MS 735, Kenneth Spencer Research Library, University of Kansas Libraries.- online: http://hdl.handle.net/10407/0546075094
F. (1998).- Dasycladacean green algae and microproblematica of the uppermost Cretaceous-Paleocene in the Karst area (NE Italy and Slovenia). In: L. & K. (eds.), Paleogene shallow benthos of the Tethys, 2.- Dela - Opera SAZU, Ljubljana, (Classis IV), p. 65-127 (16 Pls.).
J.-P. & R. (1966).- Calcareous algae from the Cretaceous and Tertiary of Cuba.- Mémoires suisses de Paléontologie, Basel, vol. 85, 47 p. (12 Pls.).
R. & P. (1982).- Les algues Dasycladales du Cénozoïque.- Bulletin du Centre de Recherche Exploration-Production elf-Aquitaine, Pau, Mémoire 4, 247 p.
R. & B. (1992).- Inventaire des Algues Dasycladales fossiles. I° partie- Les Algues Dasycladales du Tertiaire.- Revue de Paléobiologie, Genève, vol. 11, n° 2, p. 331-356.
R. & R. (1978).- Algues calcaires (Dasycladales) du Paléocène de Slovénie (Yougoslavie).- Bulletin du Centre de Recherche Exploration-Production elf-Aquitaine, Pau, vol. 2, n° 1, p. 39-60.
B. (2013).- Heteroporella ? paucicalcarea (, 1970), an Urgonian Dasycladalean alga revisited.- Carnets de Géologie [Notebooks on Geology], Brest, Letter 2013/01 (CG2013_L01), p. 59-65. DOI: 10.4267/2042/48737
B. & R. (1993).- Inventaire des Algues Dasycladales fossiles. II° partie- Les Algues Dasycladales du Jurassique et du Crétacé.- Revue de Paléobiologie, Genève, vol. 12, n° 1, p. 19-65.
B. & R. (1994).- Inventaire des Algues Dasycladales fossiles. III° partie- Les Algues Dasycladales du Permien et du Trias.- Revue de Paléobiologie, Genève, vol. 14, n° 1, p. 49-84.
I. (1967).- New Dasycladaceae from the Maastrichtian of Bepelj near Jajce (western Bosnia).- Geoloki Vjesnik, Zagreb, Svezak 20 (1966), p. 117-126 (Pls. I-VI).
J.H. & H.V. (1965).- Fossil Algae from Guatemala.- Professional Contributions of the Colorado School of Mines, Golden, n° 1, 152 p. (47 Pls.).
M.J.-F. (1995).- Pseudorhapydionina moulladei, nouveau macroforaminifère du Paléocène du Chiapas, SE Mexique.- Revue de Micropaléontologie, Paris, vol. 38, n° 2, p. 169-174-76.
R. (1990).- Paleogene dasycladalean algae from the subsurface of the Western Iraqi Desert.- Bulletin de l'Académie Serbe des Sciences et des Arts, Beograd, (Sciences mathématiques et naturelles, Sciences naturelles), t. CII, nº 32, p. 91-103.
R. (1991).- Acicularia tavnae sp. nov. and other Acetabulariaceae from the Palaeocene of eastern Majevica (NE Bosnia, Dinarides).- Geologija, Ljubljana, Knjiga 34 (vol. 34), p. 57-76.
G. (1968).- Les Cymopolia (Dasycladacées) du Thanétien des Pyrénées.- Bulletin de la Société d'Histoire naturelle de Toulouse, t. 104, fasc. 3-4, p. 381-391 (Pls. XVI-XVIII).
J.L. (1977).- Memorial to J. Harlan 1892-1974.- Memorials - Geological Society, Boulder, 6 p.
J.L. (1985).- J. Harlan (1892-1974), father of American paleoalgology. In: D.F. & M.H. (eds.), Paleoalgology; contemporary research and applications.- Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 3-8.
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
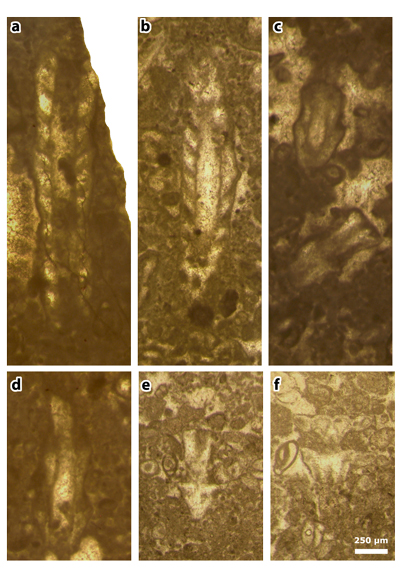
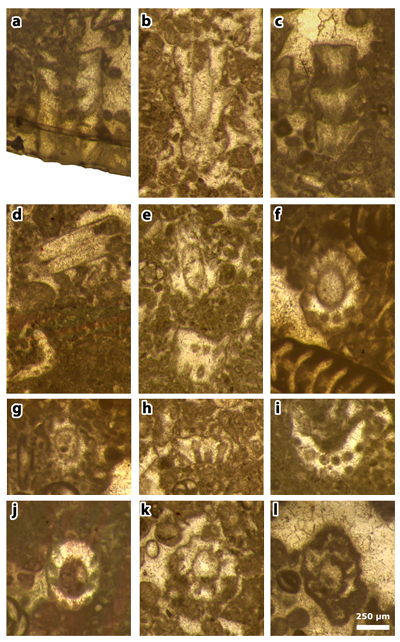
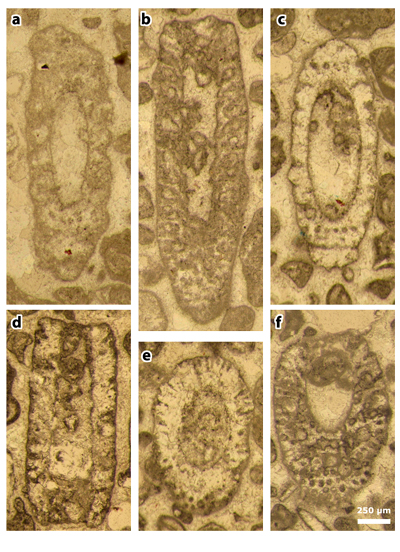
Plate 1: Figures a-f: Clypeina occidentalis & in et al., 2013 [= Clypeina occidentalis & ex & in et al., 2013, non 1965], thin section 42499. a) axial section; b) long oblique section; c) short oblique (above) and tangential (below) sections; d) axial section; e) deep tangential section (to compare with J.-P. & R. , 1966: Pl. 11, figs. 155-156); f) tangential section (to compare with , 1991: Pl. 4, fig. 2).
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
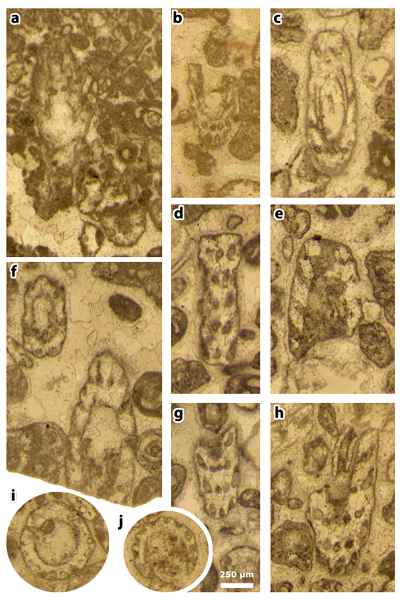
Plate 2: Figures a-l: Clypeina occidentalis & in et al., 2013 [= Clypeina occidentalis & ex & in et al., 2013, non 1965], thin section 42499. a) axial section; b) the neotype, an oblique section; c) tangential section; d) tangential section of two ( ?) laterals (above) and oblique section of a single whorl (below); e) oblique (above) and tangential (below) sections; f) oblique section (with Pseudorhapydionina moulladei , 1995); g) subtransverse section; h) oblique section of a single whorl; i) oblique section; j) subtransverse section; k) subtransverse section; l) subtransverse section.
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
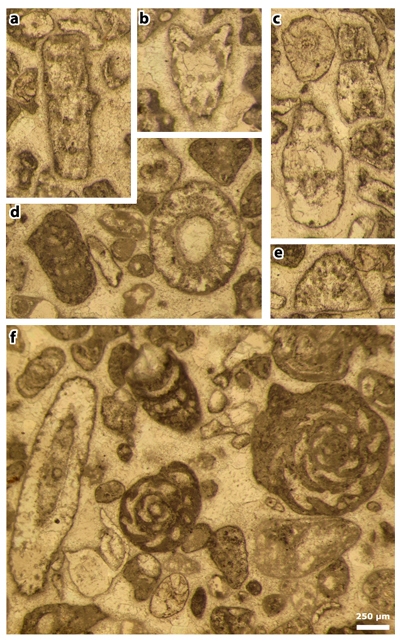
Plate 3: Figures a-j: Clypeina occidentalis & in et al., 2013 [= Clypeina occidentalis & ex & in et al., 2013, non 1965], thin sections 42499 (a) and 42504 (b-j). a) subaxial section; b) oblique section; c) oblique section; d) tangential section; e) oblique section; f) two oblique sections; g) tangential section; h) oblique section; i) subtransverse section; j) subtransverse section (this section is at the bottom of figure 3 of Plate 18 of & , 1965).
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
Plate 4: Figures a-c: Clypeina occidentalis & in et al., 2013 [= Clypeina occidentalis & ex & in et al., 2013, non 1965], thin section 42504. a) tangential section; b) tangential section; c) tangential (above) and oblique (below) sections.
Figures d-f: Cymopolia mayaense & , 1965, thin section 42504. d) oblique (subtransverse) section, with Pseudorhapydionina moulladei , 1995; e) tangential section; f) oblique (subaxial) section, with Pseudorhapydionina moulladei , 1995, and "Quasiborelis" floridanus ().
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
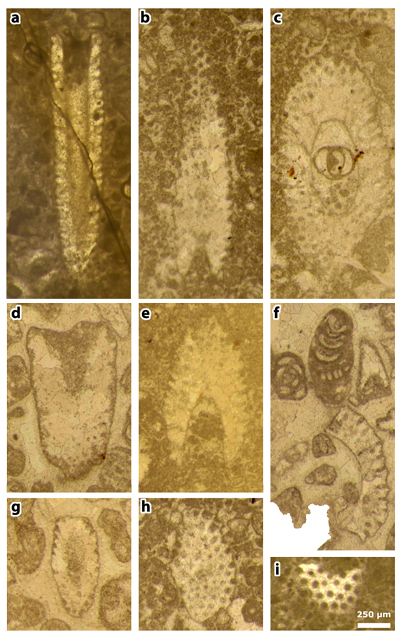
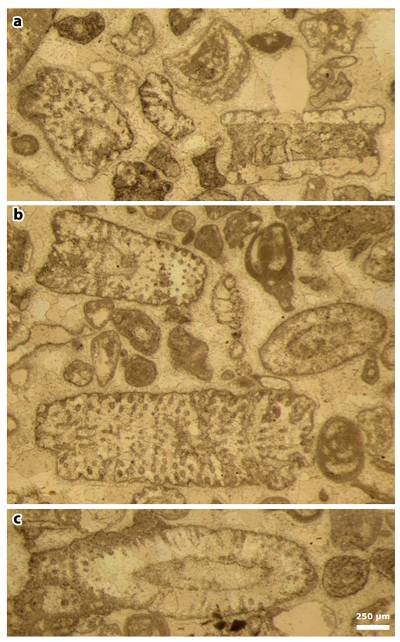
Plate 5: Figures a-i: Cymopolia mayaense & , 1965, thin sections 42499 (a-c, e & h-i) and 42504 (d & f-g). a) subaxial section; b) deep tangential section; c) oblique section; d) oblique section; e) oblique section; f) partial oblique section, with Pseudorhapydionina moulladei , 1995; g) oblique section; h) tangential section; i) tangential section.
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
Plate 6: Figures a-c: Cymopolia mayaense & , 1965, thin section 42504. a) random sections (the axial section to the right might not belong to Cymopolia); b) random sections, mostly oblique and one tangential. This last section at the bottom is herein selected as a lectotype (actually these specimens are those illustrated on figure 3 of Plate 18 of & , 1965); c) oblique section.
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
Plate 7: Figures a-f: Cymopolia mayaense & , 1965, thin section 42504. a) oblique section; b) subaxial section; c) oblique section; d) axial section; e) oblique section; f) oblique section.
Click on thumbnail to enlarge the image.
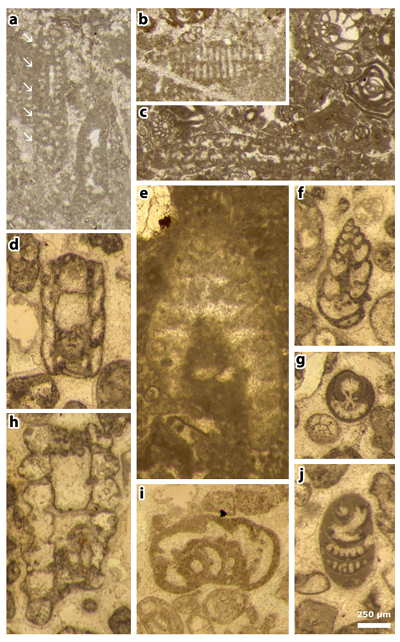
Plate 8: Figures a-c: thin section 42524. a) Cylindroporella elassonos & , 1965. The fossil pointed by the white arrows (actually the "Type" illustrated on figure 5 of Plate 18 of & , 1965) is a foraminifer, i.e., a representative either of the genus Dicyclina or of the genus Cuneolina; b) random section of a similar foraminifer; c) assemblage with Ostracoda and Foraminifera, including Dicyclina sp., Nezzazatinella picardi () and miliolids.
Figures d & f-i: thin section 42504. d) Clypeina occidentalis & in et al., 2013 [= Clypeina occidentalis & ex & in et al., 2013, non 1965], axial section; f) indetermined foraminifer (Valvulinid); g) Pseudorhapydionina moulladei , 1995, transverse section; h) Jodotella sp., axial section; i) Kayseriella cf. decastroi ; j) Pseudorhapydionina moulladei , 1995, oblique section.
Figure e: thin section 42499. Cymopolia mayaense & , 1965, oblique section.